Java program to find the LCM of two numbers – In the below-mentioned java programs, we discuss the various methods to evaluate the LCM of the two given numbers such as using Static Method, Command Line Arguments and Recursion. We also have added the compiler to each and every program along with sample outputs with specific examples.
What is LCM:
Least Common Multiplier or LCM of any n numbers is the least value that is a multiple of the given numbers.
For example:
Let us take three numbers such as 12, 15 and 18.
- 12 = 2 * 2 * 3
- 15 = 3 * 5
- 18 = 2 * 3 * 3
So we take the common prime factors and then the rest of the ones and multiply them with each other which would give us the LCM.
LCM = 2 * 2 * 3 * 3 * 5 = 180
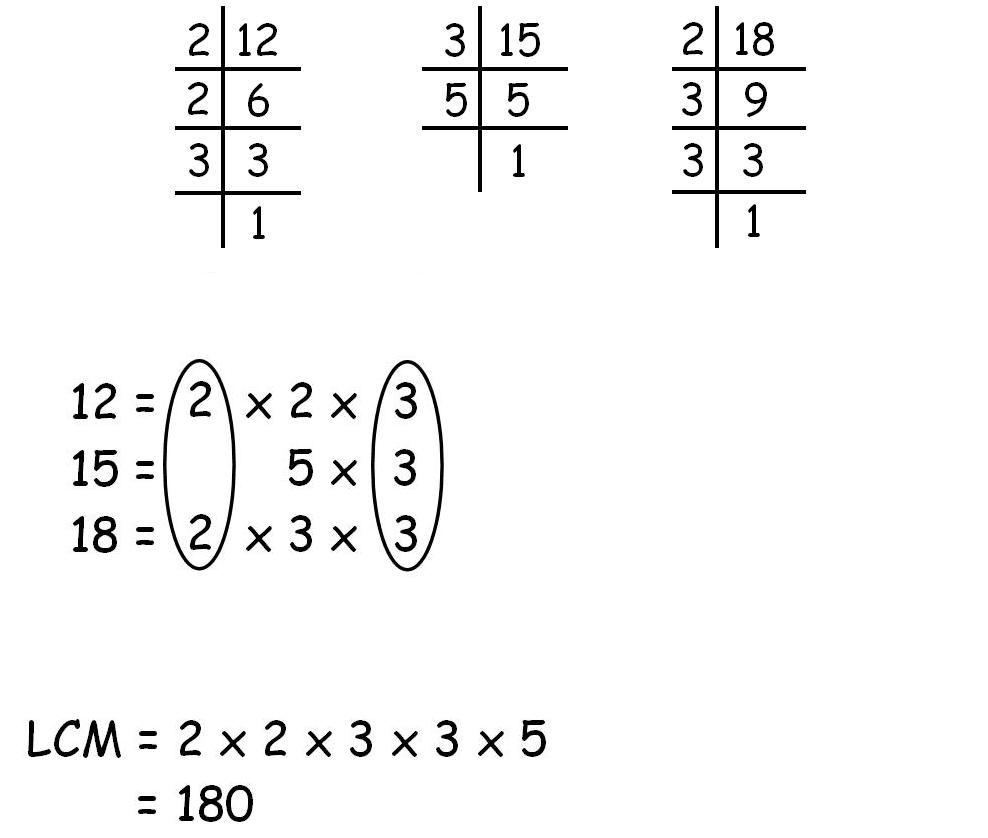
Using Static Method
1) Read the values a,b using scanner object as sc.nextInt() and store these values in the variables a,b. In this program called the static method lcmCalculation(a,b) in the main method, lcmCalculation(a,b) will calculate the lcm of two numbers.
2) The a,b values passed to n1 , n2 ,then checks the if condition ,n1>n2 then res=n1 otherwise res=n2. temp initialized to res, until the condition (res%n1!=0 || res%n2!=0) is false ,it calculates the res=temp*i;, increases the i value by 1, returns the result value.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
import java.util.Scanner; class Lcm { public static void main(String arg[]) { long a,b,lcm; Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("enter number 1"); a=sc.nextLong(); System.out.println("enter number 2"); b=sc.nextLong(); lcm=lcmCalculation(a,b); System.out.println("LCM of "+a+" and "+b+" is ="+lcm); } static long lcmCalculation(long n1,long n2) { long temp,i=2,res; if(n1>n2) res=n1; else res=n2; temp=res; while(res%n1!=0 || res%n2!=0) { res=temp*i; i++; } return res; } } |
Output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
enter number 1 125 enter number 2 4 LCM of 125 and 4 is =500 |
LCM Of Two Numbers – Using Command Line Arguments
1) The values we will pass at run-time are called command line arguments, will store at string array “String args[]” of the main method.
2) We are converting the string present at the args[0], in to long using the wrapper class “Long”, and method parseLong() and the value will store it in the variable n1.
3) We are converting the string present at the args[1], in to long using the wrapper class “Long”, and method parseLong() and the value will store it in the variable n2.
4) Checks the if condition if n1>n2 then lcm=n1 otherwise lcm=n2 and b assigned with lcm, while loop will calculate the lcm=b*i until the condition is false.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
class Lcm { public static void main(String args[]) { long n1,n2,i=2,lcm,b; n1=Long.parseLong(args[0]); n2=Long.parseLong(args[1]); if(n1>n2) lcm=n1; else lcm=n2; b=lcm; while(lcm%n1!=0 || lcm%n2!=0) { lcm=b*i; i++; } System.out.println("LCM of "+n1+" and "+n2+" is ="+lcm); } } |
Output:
|
1 2 |
>java Lcm 25 3 LCM of 25 and 3 is =75 |
Finding LCM of n numbers
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
import java.util.Scanner; class Lcm { public static void main(String s[]) { Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("enter n value"); int n=sc.nextInt(); int inputArray[]=new int[n]; System.out.println("enter "+n+" elements"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { inputArray[i]=sc.nextInt(); } long lcm=lcmCalculation(inputArray[0],inputArray[1]); for(int i=2;i<n;i++) { lcm=lcmCalculation(lcm,inputArray[i]); } System.out.println("The Least Common Multiple of "+n+" numbers is : " + lcm); } static long lcmCalculation(long n1,long n2) { long temp,i=2,res; if(n1>n2) res=n1; else res=n2; temp=res; while(res%n1!=0 || res%n2!=0) { res=temp*i; i++; } return res; } } |
Output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
enter n value 5 enter 5 elements 2 4 6 8 10 The Least Common Multiple of 5 numbers is: 120 |
Using Recursion Method
1) In this program, lcmCal(long n1,long n2,long temp,long res) method calls itself as lcmCal(n1,n2,temp,res), repeats until if condition is false ,then returns the value res.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
import java.util.Scanner; class Lcm { static int i=2; long lcmCal(long n1,long n2,long temp,long res) { if(res%n2!=0 || res%n1!=0) { res=temp*i; i=i+1; return lcmCal(n1,n2,temp,res); } return res; } public static void main(String arg[]) { long a,b,r,t,lc; Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("enter number 1"); a=sc.nextLong(); System.out.println("enter number 2"); b=sc.nextLong(); if(a==0 ||b==0) { System.out.println("Numbers should not be 0"); System.exit(0); } Lcm l=new Lcm(); if(a>b) r=a; else r=b; t=r; lc=l.lcmCal(a,b,t,r); System.out.println("LCM of 2 numbers is ="+lc); } } |
Output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
enter number 1 5 enter number 2 25 LCM of 2 numbers is =25 |
 Learn Java Java Tutoring is a resource blog on java focused mostly on beginners to learn Java in the simplest way without much effort you can access unlimited programs, interview questions, examples
Learn Java Java Tutoring is a resource blog on java focused mostly on beginners to learn Java in the simplest way without much effort you can access unlimited programs, interview questions, examples

