Merge Sort Java – Java program to implement merge sort using array & Buffered reader. Check out the list of complete Java sorting programs here.
- Using Array
- Using Buffered Reader
The compiler is also added to the aforementioned so that you can execute the program yourself, alongside suitable outputs and examples.
Merge Sort is a basic comparison based sorting algorithm which generally has Arrays as it’s data structure.
Using Array
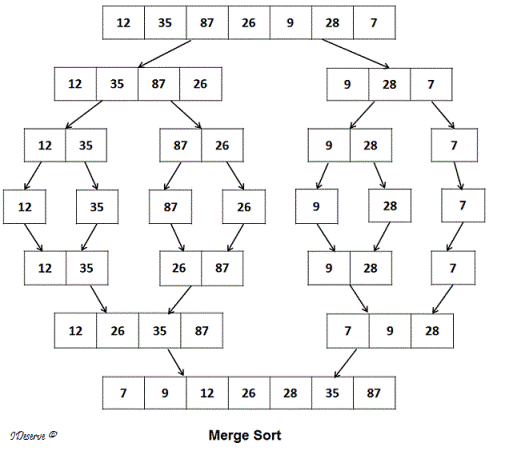
1) Merge sort combines the two sorted arrays in sorted format.
2) Sort(int a[],int l,int h) if l<h then the array will be divided in to two partitions at the index m=(l+h)/2.
One array is from index l to m, the 2nd array is from m+1 to h.
3) Sort(a,l,m) calls the sort method and again divided in to partitions until there is no possibility to next partition, and each partition will be sorted, Sort(a,m+1,h) calls the sort() method recursively until no possibility for next partition and sorted the each partition.
4) Merge method merge the partitions of the array by comparing the elements of two arrays and place the elements in order.is
In given example, the array is 12,4,0,5,3. This array will be divided into two partitions. 12,4,0 and 5,3.
12,4,0 again divided into 12 ,4 and 0. 12,4 again divided into 12 and 4 merge method sort the two partitions 12,4 and merge both partitions as 4,12, again merge method sort the two partitions 12,4 and 0 and merge both partitions as 0,4,12.
Similarly, 5,3 divided into two partitions 5,3. Merge method sort the two partitions and merge both partitions as 3,5.
Now merge method sort the two partitions 0,4,12 and 3,5 and merge these two as 0,3,4,5,12.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 |
import java.util.Scanner; public class MSort { public static void merge(int a[],int l,int m,int h) { int i, j,c=l; int b[]=new int[h+1]; for(i = l,j = m+1; i<=m && j<=h; c++) { if(a[i] <= a[j]) b[c] = a[i++]; else b[c] = a[j++]; } while(i <= m ) b[c++] = a[i++]; while(j<=h) b[c++] = a[j++]; for(i = l ; i <= h; i++) a[i] = b[i]; } public static void Sort(int a[],int l,int h) { if(l<h) { int m=(l+h)/2; Sort(a,l,m); Sort(a,m+1,h); merge(a,l,m,h); } } public static void printarray(int a[]) { for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i]+" "); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int n, res,i; Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter number of elements in the array:"); n = s.nextInt(); int a[] = new int[n]; System.out.println("Enter "+n+" elements "); for( i=0; i < n; i++) { a[i] = s.nextInt(); } System.out.println( "elements in array "); printarray(a); Sort(a,0,n-1); System.out.println( "\nelements after sorting"); printarray(a); } } |
Output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
Enter number of elements in the array:5 Enter 5 elements 12 4 0 5 3 elements in array 12 4 0 5 3 elements after sorting 0 3 4 5 12 |
Using Buffered Reader
1) readLine() method of BufferedReader class reads the data line by line.
2) BufferedReader class reads the charter as String. If we do not mention the size of the BufferedReader then it uses the default size.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 |
import java.util.Scanner; import java.io.*; public class MSort { public static void merge(int a[],int l,int m,int h) { int i, j,c=l; int b[]=new int[h+1]; for(i = l,j = m+1; i<=m && j<=h; c++) { if(a[i] <= a[j]) b[c] = a[i++]; else b[c] = a[j++]; } while(i <= m ) b[c++] = a[i++]; while(j<=h) b[c++] = a[j++]; for(i = l ; i <= h; i++) a[i] = b[i]; } public static void Sort(int a[],int l,int h) { if(l<h) { int m=(l+h)/2; Sort(a,l,m); Sort(a,m+1,h); merge(a,l,m,h); } } public static void printarray(int a[]) { for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i]+" "); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { int n,i; BufferedReader b=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.println("enter N: "); n=Integer.parseInt(b.readLine()); int a[] = new int[n]; System.out.println("enter "+n+" elements "); for(i= 0; i< n; i++) a[i] = Integer.parseInt(b.readLine()); System.out.println("elements in array "); printarray(a); Sort(a,0,n-1); System.out.println("\nelements after sorting"); printarray(a); } } |
Output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
Enter number of elements in the array:5 Enter 5 elements 12 4 0 5 3 elements in array 12 4 0 5 3 elements after sorting 0 3 4 5 12 |
More Java Programs:
 Learn Java Java Tutoring is a resource blog on java focused mostly on beginners to learn Java in the simplest way without much effort you can access unlimited programs, interview questions, examples
Learn Java Java Tutoring is a resource blog on java focused mostly on beginners to learn Java in the simplest way without much effort you can access unlimited programs, interview questions, examples

